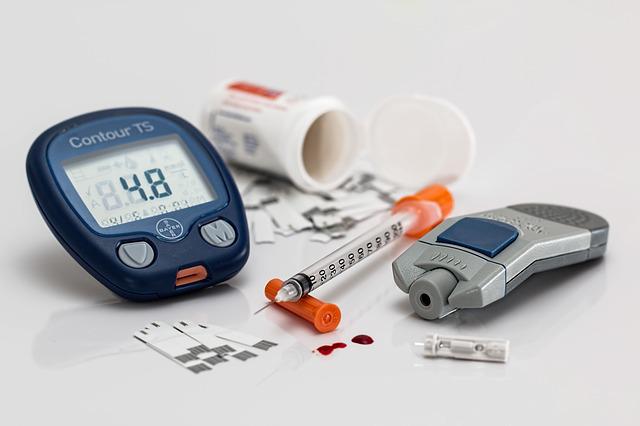
The study of the diagnosis and treatment of diabetes.
Diabetes is a long-term (chronic) illness that affects how your body converts food into energy. The majority of the food you consume is converted by your body into sugar (glucose), which is then released into your bloodstream. Your pancreas releases insulin when your blood sugar levels rise.
A chronic condition that affects the way the body processes blood sugar (glucose). With type 2 diabetes, the body either doesn't produce enough insulin, or it resists insulin. Symptoms include increased thirst, frequent urination, hunger, fatigue and blurred vision. In some cases, there may be no symptoms. Treatments include diet, exercise, medication and insulin therapy.
A chronic condition in which the pancreas produces little or no insulin. It typically appears in adolescence. Symptoms include increased thirst, frequent urination, hunger, fatigue and blurred vision. Treatment aims at maintaining normal blood sugar levels through regular monitoring, insulin therapy, diet and exercise.
A condition in which blood sugar is high, but not high enough to be type 2 diabetes. Without intervention, it's likely to become type 2 diabetes within 10 years. Many people with prediabetes have no symptoms. Progression from prediabetes to type 2 diabetes isn't inevitable. With lifestyle changes, weight loss and medication, it's possible to bring a blood sugar level back to normal.
A form of high blood sugar affecting pregnant women. Those who develop gestational diabetes are at higher risk of developing type 2 diabetes later in life. In most cases, there are no symptoms. A blood sugar test during pregnancy is used for diagnosis. Treatment strategies include daily blood sugar monitoring, a healthy diet, exercise and monitoring the baby. If blood sugar is too high, medication is required.